开源镜像安全扫描项目 —— Clair分析
1. 前言
2. Clair 架构概览
3. Clair 源码分析
- 3.1. 程序入口 main.go
- 3.2. Boot 函数
- 3.3. ProcessLayer 函数
- 3.4. detectContent 函数
- 3.5. detectFeatureVersions 函数
4. 实现自定义扫描需求的思路
附录
本文原作者为:刘梓溪(寞白)
1. 前言
Clair 是一款开源的 Docker 镜像安全扫描工具,具备对 Docker 镜像中存在的漏洞进行静态扫描的能力。
本文基于 Clair v2.0.3 Release (https://github.com/coreos/clair/archive/v2.0.3.zip) 版本源码进行分析。
本文的重点会放在 Clair 如何实现对 Docker 镜像进行静态扫描部分,并会考虑如何实现一些自定义的扫描需求。
2. Clair 架构概览
Clair 整体架构如下图所示:
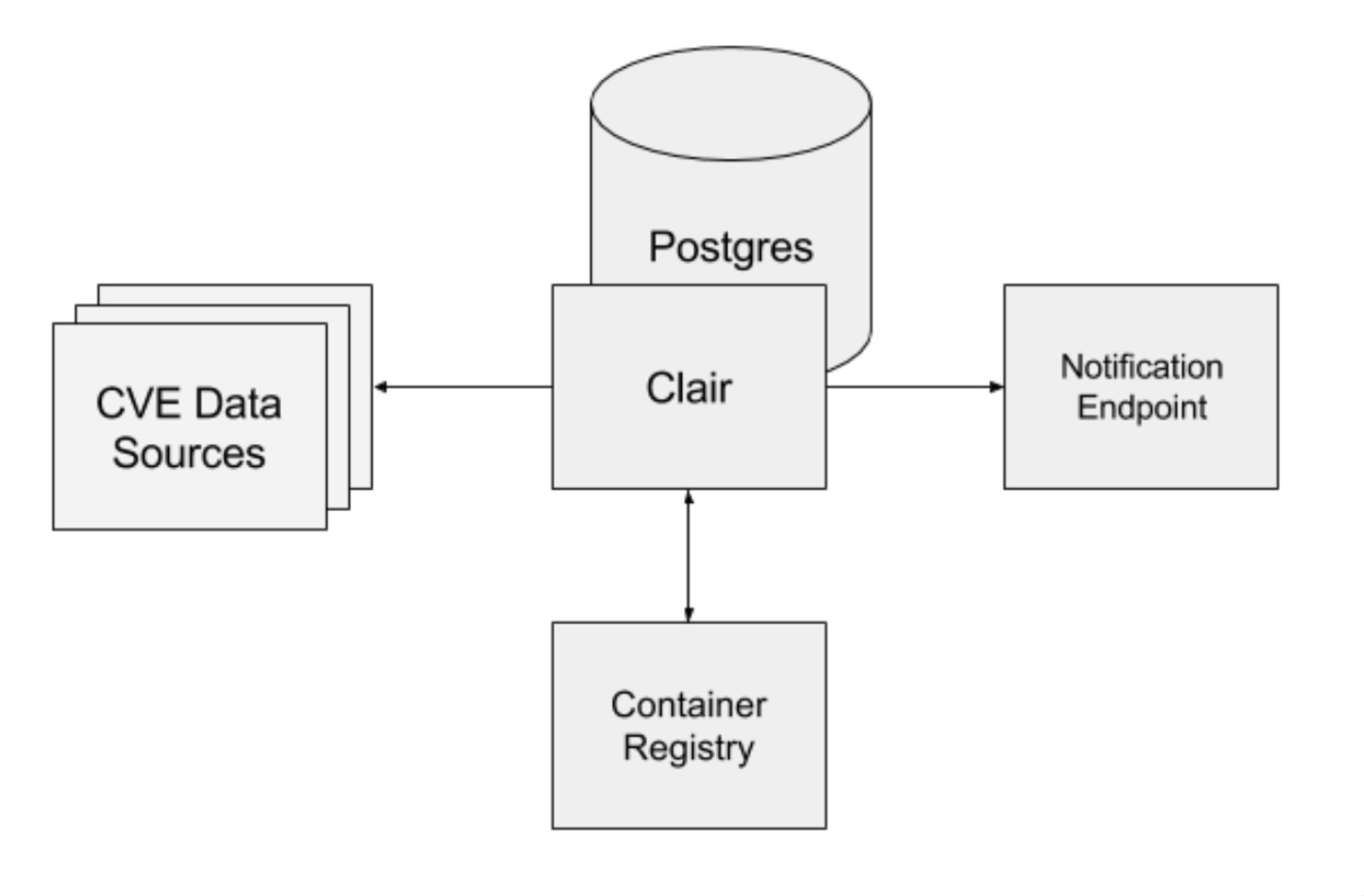 关键组件:
关键组件:api
Clair 提供一组 RESTFul API 接口,用于上传需要扫描的镜像 layer 文件,以及查询已入库的漏洞细节与漏洞修复建议。
notifier
扫描到新漏洞时,通知用户的组件。
updater
定时从漏洞源更新漏洞数据的组件。
worker
调用 POST /v1/layers 接口时,启动 worker 对 layer 文件进行扫描。
3. Clair 源码分析
3.1. 程序入口 main.go
main.go 函数接收若干 Clair 运行参数,包括:
-
cpu-profile 参数:
runtime/pprof标准库记录 CPU Profile 的文件路径,默认不记录。 -
log-level 参数: 日志等级,默认为 info
-
insecure-tls 参数: 拉取镜像 layer 时,是否使用 tls 认证,默认为 false
-
config 参数: yaml 格式的配置文件路径,定义 database, api, worker, updater, notifier 等基本组件的行为,默认路径为
/etc/clair/config.yaml
一个 yaml 配置文件的示例如下:
# Copyright 2015 clair authors
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
# The values specified here are the default values that Clair uses if no configuration file is specified or if the keys are not defined.
clair:
# 定义 Clair 使用的数据库
database:
# Database driver
type: pgsql
options:
# PostgreSQL Connection string
# https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/static/libpq-connect.html#LIBPQ-CONNSTRING
# source: host=localhost port=5432 user=postgres sslmode=disable statement_timeout=60000
source: postgresql://postgres:passw0rd@172.17.0.2:5432?sslmode=disable
# Number of elements kept in the cache
# Values unlikely to change (e.g. namespaces) are cached in order to save prevent needless roundtrips to the database.
cachesize: 16384
# 32-bit URL-safe base64 key used to encrypt pagination tokens
# If one is not provided, it will be generated.
# Multiple clair instances in the same cluster need the same value.
paginationkey:
# 定义 Clair API 行为
api:
# v3 grpc/RESTful API server address
addr: "0.0.0.0:6060"
# Health server address
# This is an unencrypted endpoint useful for load balancers to check to healthiness of the clair server.
healthaddr: "0.0.0.0:6061"
# Deadline before an API request will respond with a 503
timeout: 900s
# Optional PKI configuration
# If you want to easily generate client certificates and CAs, try the following projects:
# https://github.com/coreos/etcd-ca
# https://github.com/cloudflare/cfssl
servername:
cafile:
keyfile:
certfile:
# 定义对 layer 进行安全扫描的 worker 行为
worker:
namespace_detectors:
- os-release
- lsb-release
- apt-sources
- alpine-release
- redhat-release
feature_listers:
- apk
- dpkg
- rpm
# 定义更新漏洞库数据的行为
updater:
# Frequency the database will be updated with vulnerabilities from the default data sources
# The value 0 disables the updater entirely.
interval: 2h
enabledupdaters:
- debian
- ubuntu
- rhel
- oracle
- alpine
# 定义通知组件的行为
notifier:
# Number of attempts before the notification is marked as failed to be sent
attempts: 3
# Duration before a failed notification is retried
renotifyinterval: 2h
http:
# Optional endpoint that will receive notifications via POST requests
endpoint:
# Optional PKI configuration
# If you want to easily generate client certificates and CAs, try the following projects:
# https://github.com/cloudflare/cfssl
# https://github.com/coreos/etcd-ca
servername:
cafile:
keyfile:
certfile:
# Optional HTTP Proxy: must be a valid URL (including the scheme).
proxy:在完成运行参数解析后,会调用 Boot 函数运行几个关键 goroutine
3.2. Boot 函数
函数定义:
func Boot(config *Config)Boot 函数中启动了四个 goroutine,并通过一个全局的 stop chan 来控制各个 goroutine 的生命周期。
四个 goroutine 分别为:
- api: 提供 Clair 的 RESTFul API 服务
- api-healthcheck: api 的健康检查
- notifier: 扫描到新漏洞时,通知用户的组件
- updater: 定时从漏洞源更新漏洞数据的组件
其中 api-healthcheck notifier updater 不在本文的重点讨论范围内,不展开讨论了。
api goroutine 中运行了 Clair 提供服务的 RESTFul 接口,具体接口细节可以参考:https://coreos.com/clair/docs/latest/api_v1.html
其中,关键接口是 POST /v1/layer,它用于传入指定 Docker 镜像的 layer 并进行安全扫描。
该接口的处理函数为 postLayer,在 postLayer 函数内部调用 ProcessLayer 函数对 layer 进行扫描。
该接口具备以下必备参数:
{
"Layer": {
"Name": "523ef1d23f222195488575f52a39c729c76a8c5630c9a194139cb246fb212da6",
"Path": "https://mystorage.com/layers/523ef1d23f222195488575f52a39c729c76a8c5630c9a194139cb246fb212da6/layer.tar",
"ParentName": "140f9bdfeb9784cf8730e9dab5dd12fbd704151cf555ac8cae650451794e5ac2",
"Format": "Docker"
}
}
- Name: 当前 layer 的 sha256 摘要名称
- Path: 当前 layer 的访问路径
- ParentName: 当前 layer 的父辈 layer 的名称
- Format: layer 的格式,目前支持 Docker 与 appc
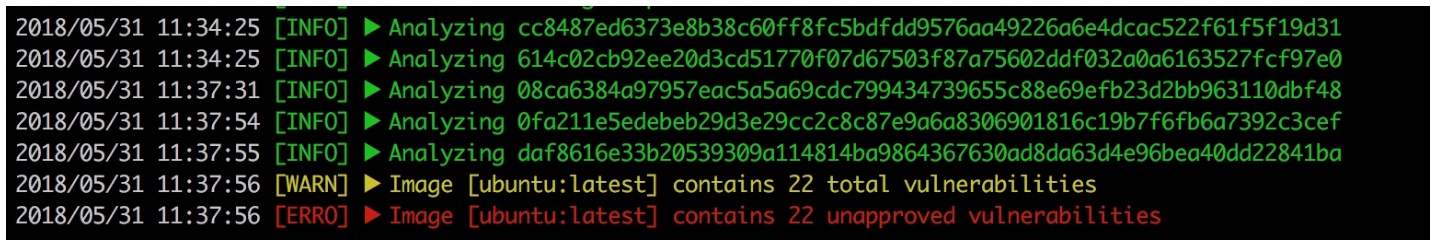
对于一个完整的 Docker 镜像,需要逐级提交构成镜像的 layer 进行分析。本文中使用 ubuntu 作为测试镜像,该镜像包含 5 个 layer,所以对 ubuntu 镜像完成扫描需要按照 layer 的继承关系,依次进行 5 次请求:
3.3. ProcessLayer 函数
函数定义:
func ProcessLayer(datastore database.Datastore, imageFormat, name, parentName, path string, headers map[string]string) errorProcessLayer 函数首先从数据库中查询当前的 layer 是否已经有过之前的扫描结果。
- 如果有的话直接返回
- 如果没有的话,首先会判断 parentName 所指定的 parent layer 是否在数据库中已有扫描结果。如果没有的话,会抛出异常。如果有的话,会调用 detectContent 函数对 layer 文件进行扫描,并将扫描结果入库。
3.4. detectContent 函数
函数定义:
func detectContent(imageFormat, name, path string, headers map[string]string, parent *database.Layer) (namespace *database.Namespace, featureVersions []database.FeatureVersion, err error)
detectContent 函数内部处理过程如下:
-
根据 imageFormat 格式,调用对应的 imagefmt.Extract 接口,将 layer 文件保存到
files变量中 (数据格式为:tarutil.FilesMap) -
传入 layerName, parentName, files 调用
detectNamespace函数,判断当前 layer 需要在什么上下文中,扫描漏洞。(namespace: a context around features and vulnerabilities (e.g. an operating system or a programming language) -
传入 layerName, parentName, files, namespace 调用
detectFeatureVersions函数,扫描是否存在已知漏洞的 feature (feature: anything that when present in a filesystem could be an indication of a vulnerability (e.g. the presence of a file or an installed software package)) -
返回
detectFeatureVersions函数的扫描结果。
其中,在第一步中解析出来的 layer 文件,其数据格式为 tarutil.FilesMap (map[string][]byte)
为了更好的探究 layer 中的文件内容,我们在 detectContent 函数中添加以下代码帮助我们调试,将 files 里的文件输出到本地硬盘中:
for key, value := range files {
os.Mkdir("~/tmp/clair/files/" + name, 0777)
f, _ := os.Create(fmt.Sprintf("~/tmp/clair/files/%s/%s", name, strings.Replace(key, "/", "___", -1)))
f.Write(value)
f.Close()
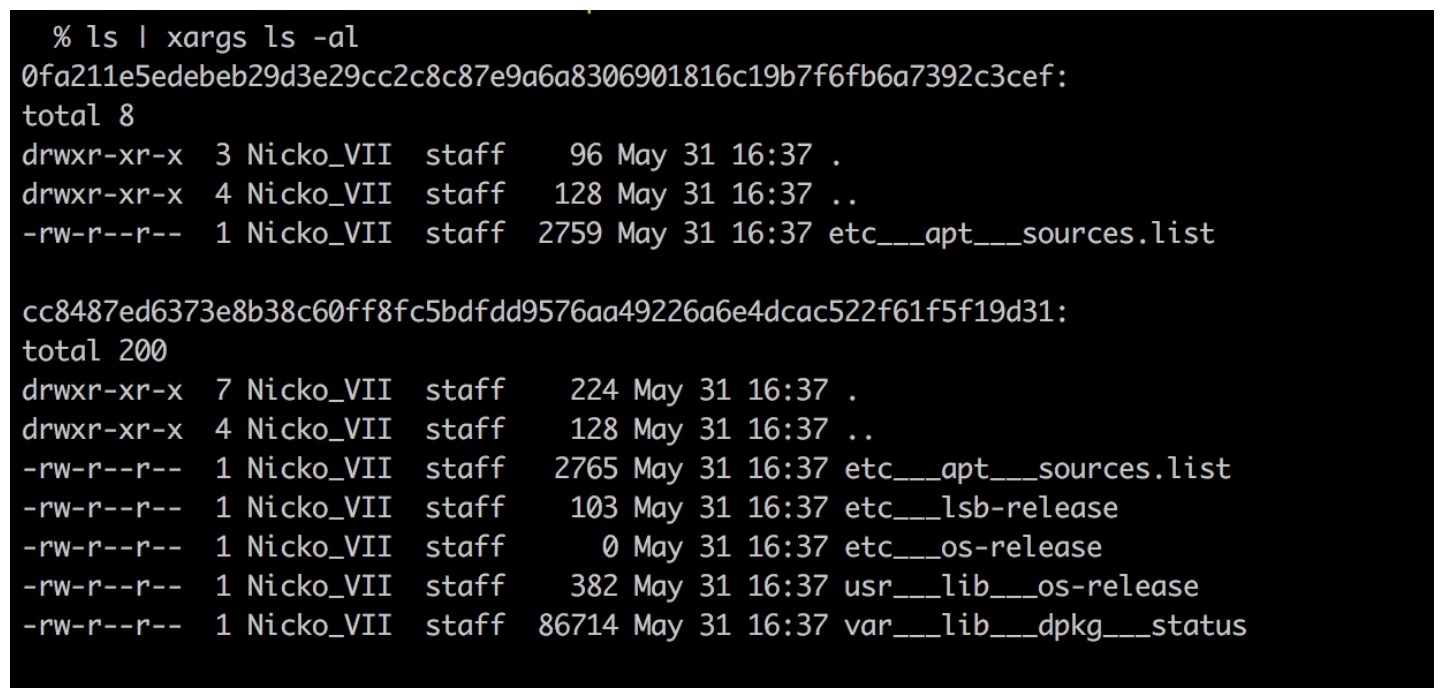
}输出如下,可以看到 ubuntu 镜像中的以下 5 个 layer 中:
- cc8487ed6373e8b38c60ff8fc5bdfdd9576aa49226a6e4dcac522f61f5f19d31
- 614c02cb92ee20d3cd51770f07d67503f87a75602ddf032a0a6163527fcf97e0
- 08ca6384a97957eac5a5a69cdc799434739655c88e69efb23d2bb963110dbf48
- 0fa211e5edebeb29d3e29cc2c8c87e9a6a8306901816c19b7f6fb6a7392c3cef
- daf8616e33b20539309a114814ba9864367630ad8da63d4e96bea40dd22841ba
第一层 layer: cc8487ed6373e8b38c60ff8fc5bdfdd9576aa49226a6e4dcac522f61f5f19d31,与第四层 layer: 0fa211e5edebeb29d3e29cc2c8c87e9a6a8306901816c19b7f6fb6a7392c3cef,中包含文件
3.5. detectFeatureVersions 函数
源码分析
func detectFeatureVersions(name string, files tarutil.FilesMap, namespace *database.Namespace, parent *database.Layer) (features []database.FeatureVersion, err error) {
// 调用所有已经注册了的 featurefmt 插件, 对 files 进行扫描
// 目前默认集成的插件有 apt, rpm, dpkg
features, err = featurefmt.ListFeatures(files)
if err != nil {
return
}
// 如果当前 layer 未扫描到 feature,尝试返回 parent layer 的 feature
if len(features) == 0 && parent != nil {
features = parent.Features
return
}
// Build a map of the namespaces for each FeatureVersion in our parent layer.
parentFeatureNamespaces := make(map[string]database.Namespace)
if parent != nil {
for _, parentFeature := range parent.Features {
parentFeatureNamespaces[parentFeature.Feature.Name+":"+parentFeature.Version] = parentFeature.Feature.Namespace
}
}
// 确保每一个 feature 都能关联到一个 namespace 上
for i, feature := range features {
if feature.Feature.Namespace.Name != "" {
// There is a Namespace associated.
continue
}
if parentFeatureNamespace, ok := parentFeatureNamespaces[feature.Feature.Name+":"+feature.Version]; ok {
// The FeatureVersion is present in the parent layer; associate with their Namespace.
features[i].Feature.Namespace = parentFeatureNamespace
continue
}
if namespace != nil {
// The Namespace has been detected in this layer; associate it.
features[i].Feature.Namespace = *namespace
continue
}
log.WithFields(log.Fields{"feature name": feature.Feature.Name, "feature version": feature.Version, logLayerName: name}).Warning("Namespace unknown")
err = ErrUnsupported
return
}
return
}
可见 detectFeatureVersions 函数中,扫描 feature 的部分,在 featurefmt.ListFeatures 方法中实现。
// ListFeatures produces the list of FeatureVersions in an image layer using// every registered Lister.func ListFeatures(files tarutil.FilesMap) ([]database.FeatureVersion, error) {
listersM.RLock()
defer listersM.RUnlock()
var totalFeatures []database.FeatureVersion
for _, lister := range listers {
features, err := lister.ListFeatures(files)
if err != nil {
return []database.FeatureVersion{}, err
}
totalFeatures = append(totalFeatures, features...)
}
return totalFeatures, nil
}
其中 lister 是一个 Lister 类型接口, 如之前提到,默认集成了 apt, rpm, dpkg 这三个检测插件。
本文中以 ubuntu 镜像作为示例,故只看一下 dpkg 插件的 ListFeatures() 函数实现。
以下是 dpkg 插件的 ListFeatures 函数实现代码:
func (l lister) ListFeatures(files tarutil.FilesMap) ([]database.FeatureVersion, error) {
f, hasFile := files["var/lib/dpkg/status"]
if !hasFile {
return []database.FeatureVersion{}, nil
}
// Create a map to store packages and ensure their uniqueness
packagesMap := make(map[string]database.FeatureVersion)
var pkg database.FeatureVersion
var err error
scanner := bufio.NewScanner(strings.NewReader(string(f)))
for scanner.Scan() {
line := scanner.Text()
if strings.HasPrefix(line, "Package: ") {
// Package line
// Defines the name of the package
pkg.Feature.Name = strings.TrimSpace(strings.TrimPrefix(line, "Package: "))
pkg.Version = ""
} else if strings.HasPrefix(line, "Source: ") {
// Source line (Optionnal)
// Gives the name of the source package
// May also specifies a version
srcCapture := dpkgSrcCaptureRegexp.FindAllStringSubmatch(line, -1)[0]
md := map[string]string{}
for i, n := range srcCapture {
md[dpkgSrcCaptureRegexpNames[i]] = strings.TrimSpace(n)
}
pkg.Feature.Name = md["name"]
if md["version"] != "" {
version := md["version"]
err = versionfmt.Valid(dpkg.ParserName, version)
if err != nil {
log.WithError(err).WithField("version", string(line[1])).Warning("could not parse package version. skipping")
} else {
pkg.Version = version
}
}
} else if strings.HasPrefix(line, "Version: ") && pkg.Version == "" {
// Version line
// Defines the version of the package
// This version is less important than a version retrieved from a Source line
// because the Debian vulnerabilities often skips the epoch from the Version field
// which is not present in the Source version, and because +bX revisions don't matter
version := strings.TrimPrefix(line, "Version: ")
err = versionfmt.Valid(dpkg.ParserName, version)
if err != nil {
log.WithError(err).WithField("version", string(line[1])).Warning("could not parse package version. skipping")
} else {
pkg.Version = version
}
} else if line == "" {
pkg.Feature.Name = ""
pkg.Version = ""
}
// Add the package to the result array if we have all the informations
if pkg.Feature.Name != "" && pkg.Version != "" {
packagesMap[pkg.Feature.Name+"#"+pkg.Version] = pkg
pkg.Feature.Name = ""
pkg.Version = ""
}
}
// Convert the map to a slice
packages := make([]database.FeatureVersion, 0, len(packagesMap))
for _, pkg := range packagesMap {
packages = append(packages, pkg)
}
return packages, nil
}
可以看到,dpkg 插件中,主要是扫描 var/lib/dpkg/status 这个文件的内容,判断 dpkg 包是否是存在漏洞的版本 (下面是一段 var/lib/dpkg/status 的文件示例)
Package: fdisk
Status: install ok installed
Priority: important
Section: utils
Installed-Size: 426
Maintainer: Ubuntu Developers <ubuntu-devel-discuss@lists.ubuntu.com>
Architecture: amd64
Multi-Arch: foreign
Source: util-linux
Version: 2.31.1-0.4ubuntu3
Replaces: util-linux (<< 2.30.1-0ubuntu4~)
Depends: libc6 (>= 2.14), libfdisk1 (>= 2.31.1), libmount1 (>= 2.24.2), libncursesw5 (>= 6), libsmartcols1 (>= 2.28~rc1), libtinfo5 (>= 6)
Breaks: util-linux (<< 2.30.1-0ubuntu4~)
Description: collection of partitioning utilities
This package contains the classic fdisk, sfdisk and cfdisk partitioning
utilities from the util-linux suite.
.
The utilities included in this package allow you to partition
your hard disk. The utilities supports both modern and legacy
partition tables (eg. GPT, MBR, etc).
.
The fdisk utility is the classical text-mode utility.
The cfdisk utilitity gives a more userfriendly curses based interface.
The sfdisk utility is mostly for automation and scripting uses.
Important: yes
Original-Maintainer: LaMont Jones <lamont@debian.org>
Package: libpam-runtime
Status: install ok installed
Priority: requiredSection: admin
Installed-Size: 300
Maintainer: Ubuntu Developers <ubuntu-devel-discuss@lists.ubuntu.com>
Architecture: all
Multi-Arch: foreign
Source: pam
Version: 1.1.8-3.6ubuntu2
Replaces: libpam0g-dev, libpam0g-util
Depends: debconf (>= 0.5) | debconf-2.0, debconf (>= 1.5.19) | cdebconf, libpam-modules (>= 1.0.1-6)
Conflicts: libpam0g-util
Conffiles:
/etc/pam.conf 87fc76f18e98ee7d3848f6b81b3391e5
/etc/pam.d/other 31aa7f2181889ffb00b87df4126d1701
Description: Runtime support for the PAM library
Contains configuration files and directories required for
authentication to work on Debian systems. This package is required
on almost all installations.
Homepage: http://www.linux-pam.org/
Original-Maintainer: Steve Langasek <vorlon@debian.org>
4. 实现自定义扫描需求的思路
从第三部分可以看到,Clair 的漏洞扫描功能,大致流程为解析出镜像中各个 layer 中的文件内容,然后通过分析一些关键文件的内容,判断是否可能存在漏洞。
如果要实现一些自定义的扫描需求,只需要编写一个 featurefmt 插件,并按照 Clair 框架定义的接口格式,实现对于各个 layer 文件内容的扫描逻辑即可。
附录
参考
- Clair API: https://coreos.com/clair/docs/latest/api_v1.html
- Clair Documentation: https://github.com/coreos/clair/tree/master/Documentation
- Clair-Scanner: https://github.com/arminc/clair-scanner
名词解释
Docker 相关
Container: the execution of an imageImage: a set of tarballs that contain the filesystem contents and run-time metadata of a containerLayer: one of the tarballs used in the composition of an image, often expressed as a filesystem delta from another layer
Clair 相关
Ancestry: the Clair-internal representation of an ImageFeature: anything that when present in a filesystem could be an indication of a vulnerability (e.g. the presence of a file or an installed software package)Feature Namespace (featurens): a context around features and vulnerabilities (e.g. an operating system or a programming language)Vulnerability Source (vulnsrc): the component of Clair that tracks upstream vulnerability data and imports them into Clair's databaseVulnerability Metadata Source (vulnmdsrc): the component of Clair that tracks upstream vulnerability metadata and associates them with vulnerabilities in Clair's database